Error distributions – thermolib.error
- class thermolib.error.ErrorArray(errors, axis=0)[source]
A class to represent an array of independent error distributions. This class is used to store the distributiosn for errors on the conditional probabilities, i.e. for each value of cv in p(q|cv) there is an error distribution. The error distribution on p(q|cv1) is assumed uncorrelated with that of p(q|cv2), but we still want to store the distribution for the errors for each cv value in one object.
- Parameters:
errors (list of instances of
Distribution) – list of error distirbutions to be storedaxis (int, optional, default=0) – the axis index along which the errors are stacked. Only two valid choices: 0 and -1
- mean()[source]
Return the distribution mean for each element in the errors list
- Returns:
mean of the distibution
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- nsigma_conf_int(nsigma)[source]
Compute the n-sigma confidence interval, i.e.
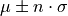 , for each element in the errors list
, for each element in the errors list- Returns:
mean of the distibution
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- sample(nsamples=None)[source]
Returns a number of random samples taken according to the error distribution for each element in the error list
- Parameters:
nsamples (int or None, optional, default=None) – the number of samples returned. If None, a single sample will be returned and the shape of the return value will be identical to self.means and self.stds. If not None, the return value will have an additional dimension with size given by nsamples.
- Returns:
multidimensional numpy array containing random samples for each element in self.errors. Shape of this array depends on nsamples, self.naxis and number of elements in self.errors.
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- class thermolib.error.GaussianDistribution(means, stds)[source]
Implementation of a Gaussian distribution defined by its mean and standard deviation.
- Parameters:
means (int, float or np.ndarray) – mean (or means if multidimensional) of the Gaussian distribution
stds (int, float or np.ndarray) – standard deviation (or standard deviations if multidimensional) of the Gaussian distribution
- Raises:
ValueError – if means is not an integer, float or np.ndarray
AssertionError – if means and stds do not have same shape
- classmethod from_samples(samples)[source]
Defines a GaussianDistribution based on a population defined by the given samples. The routine will derive the mean and std from the population and use that to define the Gaussian Distribution.
- Parameters:
samples (np.ndarray) – the samples that define the population
- classmethod log_from_loggaussian(logdist, shift=0.0, scale=1.0)[source]
Define the Gaussian distribution of a variable
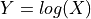 in which
in which 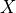 has a given LogGaussian distribution, potential after imposing a shift and rescaling.
has a given LogGaussian distribution, potential after imposing a shift and rescaling.- Parameters:
logdist (
LogGaussianDistribution) – the LogGaussian distribution of variable X in the expression above.shift (float, optional, default=0.0) – shift to be applied to the mean upon conversion
scale (float, optional, default=1.0) – rescaling to be applied to the mean and std upon conversion
- Raises:
AssertionError – if the given logdist is not an instance of
LogGaussianDistribution
- mean()[source]
Return the distribution mean
- Returns:
mean of the distibution
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- nsigma_conf_int(nsigma)[source]
Compute the n-sigma confidence interval, i.e.
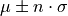
- Parameters:
nsigma (int, optional, default=2) – value of n in the above formula
- print(fmt='%.3f', unit='au', do_scientific=False, nsigma=2)[source]
Routine to print the statistical properties of a scalar quantity.
- Parameters:
fmt (str, optional, default='%.3f') – python string formatting for how to format floats (such as the mean and error). This argument is ignored if
do_scientificis set tot True.unit (str, optional, default='au') – unit in which to print the current quantity.
do_scientific (bool, optional, default=False) – use scientific formatting of floats
nsigma (int, optional, default=2) – print error bars as
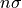 error bars. Hence, setting
error bars. Hence, setting nsigma=2will return error bars that are twice the standard deviation resulting from the error distribution.
- sample(nsamples=None)[source]
Returns a number of random samples from the population defined by the Gaussian distribution
- Parameters:
nsamples (int or None, optional, default=None) – the number of samples returned. If None, a single sample will be returned and the shape of the return value will be identical to self.means and self.stds. If not None, the return value will have an additional dimension with size given by nsamples.
- Returns:
a (set of) random sample(s) from the population
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- set_ref(index=None, value=None)[source]
Set reference of distribution means by shifting them over an amount equal to -value or -self.means[index].
- Parameters:
index (int, optional, default=None) – shift distribution means over an amount equal -self.means[index]. Ignored if set to None.
value (type consistent with population samples, optional, default=None) – shift distribution means over an amount equal to -value. Ignored if index is not None.
- Raises:
ValueError – if both index and value are set to None
- class thermolib.error.LogGaussianDistribution(lmeans, lstds)[source]
Implementation of a Log-Gaussian distribution, i.e. variable X is Log-Gaussian with mean lmu and std lsigma if variable log(X) is Gaussian distributed with mean lmu and std lsigma.
- Parameters:
lmeans – mean (or means if multidimensional) of the corresponding Gaussian distribution of log(X)
lstds – standard deviation (or standard deviations if multidimensional) of the corresponding Gaussian distribution of log(X)
- Raises:
ValueError – if lmeans is not an integer, float or np.ndarray
AssertionError – if lmeans and lstds do not have same shape
- classmethod exp_from_gaussian(gaussdist, shift=0.0, scale=1.0)[source]
Define the LogGaussian distribution of a variable
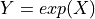 in which
in which 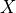 has a given Gaussian distribution, potential after imposing a shift and rescaling.
has a given Gaussian distribution, potential after imposing a shift and rescaling.- Parameters:
gaussdist (
GaussianDistribution) – the Gaussian distribution of variable X in the expression above.shift (float, optional, default=0.0) – shift to be applied to the mean upon conversion
scale (float, optional, default=1.0) – rescaling to be applied to the mean and std upon conversion
- Raises:
AssertionError – if the given gaussdist is not an instance of
GaussianDistribution
- classmethod from_samples(samples)[source]
Defines a LogGaussianDistribution based on a population defined by the given samples. The routine will derive lmean and lstd from the log of the given population samples and use that to define the LogGaussian Distribution.
- Parameters:
samples (np.ndarray) – the samples that define the population
- mean()[source]
Return the distribution mean
- Returns:
mean of the distibution
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- nsigma_conf_int(nsigma)[source]
Compute the n-sigma confidence interval, i.e.
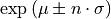
- Parameters:
nsigma (int, optional, default=2) – value of n in the above formula
- sample(nsamples=None)[source]
Returns a number of random samples from the population defined by the distribution
- Parameters:
nsamples (int or None, optional, default=None) – the number of samples returned. If None, a single sample will be returned and the shape of the return value will be identical to self.means and self.stds. If not None, the return value will have an additional dimension with size given by nsamples.
- Returns:
a (set of) random sample(s) from the population
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- set_ref(index=None, value=None)[source]
Set reference of distribution lmeans (NOT THE DISTRIBUTION MEANS!!) by shifting them over an amount equal to -value or -self.lmeans[index].
- Parameters:
index (int, optional, default=None) – shift distribution lmeans over an amount equal -self.lmeans[index]. Ignored if set to None.
value (type consistent with population samples, optional, default=None) – shift distribution lmeans over an amount equal to -value. Ignored if index is not None.
- Raises:
ValueError – if both index and value are set to None
- class thermolib.error.MultiDistribution(shape, flattener=<thermolib.flatten.DummyFlattener object>)[source]
Abstract parent class for probability distributions of multidimensional stochastic properties used for error propagation. This class will explicitly account for correlation across the dimensions, as such it can be used to account for the correlation between the free energy at two different points in a FEP. Most of the routines here are implemented in the child classes.
- Parameters:
shape (list of integers) – the dimensions of the property for which the distribution is stored
flattener (
Flattener, optional, default=None) – The flattener encodes how to flatten the multidimensional properties stored in nD-arrays into a longer 1D-array for easiear error propagation. This flattener also allows to do the inverse transformation, i.e. deflatten the flattened 1D-array back to its original nD-array format.
- corr(unflatten=True)[source]
Routine that will convert the covariance matrix computed with self.cov to a correlation matrix according to the formula
![Cor[i,j] &= \frac{Cov[i,j]}{\sigma_i \sigma_j}](_images/math/22b5d1a898ff523ff8764894386a1cb24375c39a.png)
in which
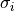 is the standard deviation of the i-th quantity in the multidimensional stochastic property.
is the standard deviation of the i-th quantity in the multidimensional stochastic property.- Parameters:
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return the correlation matrix in a shape equal to ‘the square’ of in the original dimensional shape. If False, return the correlation matrix as a flattened 2D array.
- class thermolib.error.MultiGaussianDistribution(means, covariance, flattener=<thermolib.flatten.DummyFlattener object>)[source]
Implementation of a multivariate normal distribution for a given vector of means and a given covariance matrix
- Parameters:
means (np.ndarray) – means of the multivariate normal distribution
covariance (np.ndarray with a dimension equal tot the square of means, i.e. if means.shape=(N,) then covariance.shape=(N,N) and if means.shape=(K,L) then covariance.shape=(K,L,K,L).) – covariance matrix of the multivariate normal distribution
flattener (
Flattener, optional, default=DummyFlattener() indicating no flattening) – The flattener encodes how to flatten the multidimensional properties stored in nD-arrays into a longer 1D-array for easiear error propagation. This flattener also allows to do the inverse transformation, i.e. deflatten the flattened 1D-array back to its original nD-array format. Should be specified if len(means.shape)=1 because it represents a flattened 2D array (which also implies len(covariance.shape)=2 because it represents a flattened 4D array).
- cov(unflatten=True)[source]
Return the covariance matrix of the MultiGaussian distribution.
- Parameters:
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return the covariance matrix in a shape equal to ‘the square’ of in the original dimensional shape. If False, return the covariance matrix as a flattened 2D array.
- classmethod from_samples(samples, flattener=<thermolib.flatten.DummyFlattener object>, flattened=True)[source]
Defines a MultiGaussianDistribution based on a population defined by the given samples. The routine will derive the mean and std from the population and use that to define the Gaussian Distribution.
- Parameters:
samples (np.ndarray) – the samples that define the population
flattened (bool, optional, default=False) –
If flattened is True, the given samples should be a 2D array in which a row represents all observations of a single variable and a column represents a single observation of all variables.
If flattened is False, then the the samples array is assumed to be 3 dimensional for which the first two dimensions represent a 2D index and the third index is the sample index. Therefore, the flattener will first be applied to flatten the 2D index into a 1D index and hence convert the samples to a 2D array of the same shape as required if the flattened argument is True.
- Raises:
AssertionError – if the dimensions of samples array are invalid
- classmethod log_from_loggaussian(logdist, shift=0.0, scale=1.0)[source]
Define the MultiGaussian distribution of a variable
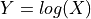 in which
in which 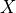 has a given MultiLogGaussian distribution, potential after imposing a shift and rescaling.
has a given MultiLogGaussian distribution, potential after imposing a shift and rescaling.- Parameters:
logdist (
MultiLogGaussianDistribution) – the MultiLogGaussian distribution of variable X in the expression above.shift (float, optional, default=0.0) – shift to be applied to the mean upon conversion
scale (float, optional, default=1.0) – rescaling to be applied to the mean and std upon conversion
- Raises:
AssertionError – if logdist is not instance of
MultiLogGaussianDistribution
- mean(unflatten=True)[source]
Return the distribution mean
- Parameters:
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return the distribution mean in the original dimensional shape. If False, return the distribution mean as a flattened 1D array.
- Returns:
mean of the distibution
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- nsigma_conf_int(nsigma=2, unflatten=True)[source]
Compute the n-sigma confidence interval, i.e.
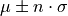
- Parameters:
nsigma (int, optional, default=2) – value of n in the above formula
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return the interval in the original dimensional shape. If False, return as a flattened 1D array.
- plot_corr_matrix(fn=None, fig_size_inches=[8, 8], cmap='bwr', logscale=False, cvs=None, nticks=10, decimals=1)[source]
gMake a plot of the correlation matrix of the current multivariate Gaussian distribution
- Parameters:
fn (_type_, optional, default=None) – file name to which figure will be saved. If None, figure will note be written to file.
fig_size_inches (list, optional, default=[8,8]) – [x,y]-dimensions of the figure in inches
cmap (str, optional, default='bwr') – color map to be used, see matplotlib documentation to see possibilities.
logscale (bool, optional, default=False) – plot correlation in logarithmic scale
cvs (np.ndarray, optional, default=None) – set x and y-tick labels to CV values given in cvs
nticks (int, optional, default=10) – number of ticks on x and y-axis. Only used when parameter cvs is given.
decimals (int, optional, default=1) – number of decimals to be shown in CV tick labels. Only used when parameter cvs is given.
- sample(nsamples=None, unflatten=True)[source]
Returns a number of random samples from the population defined by the distribution
- Parameters:
nsamples (int or None, optional, default=None) – the number of samples returned. If None, a single sample will be returned with a shape depending on whether or not it is flattened (see parameter unflatten). If not None, the return value will have an additional dimension with size given by nsamples.
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return each distribution sample in the original dimensional shape. If False, return each sample as a flattened 1D array.
- Returns:
a (set of) random sample(s) from the population
- Return type:
np.ndarray whose dimension depend on the nsamples and unflatten keyword values. If nsamples is None, a single sample is returned whose shape depends on whether or not it is flattened (see parameter unflatten). If nsamples is not None, the return value will have an additinal dimension with size given by nsamples.
- set_ref(index=None, value=None)[source]
Set reference of distribution means by shifting them over an amount equal to -value or -self.means[index].
- Parameters:
index (tuple|list, optional, default=None) – shift distribution means over an amount equal -self.means[index]. Ignored if set to None.
value (type consistent with population samples, optional, default=None) – shift distribution means over an amount equal to -value. Ignored if index is not None.
- Raises:
ValueError – if both index and value are set to None
- std(unflatten=True)[source]
Return the distribution standard deviation (std)
- Parameters:
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return the distribution std in the original dimensional shape. If False, return the distribution std as a flattened 1D array.
- Returns:
standard deviation of the distibution
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- class thermolib.error.MultiLogGaussianDistribution(lmeans, lcovariance, flattener=<thermolib.flatten.DummyFlattener object>)[source]
Implementation of a multivariate log-normal distribution for a given vector of means and a given covariance matrix
- Parameters:
means (np.ndarray) – lmeans of the multivariate log-normal distribution, i.e. means of the underlying normal distribution of log(X)
covariance (np.ndarray with a dimension equal tot the square of means, i.e. if means.shape=(N,) then covariance.shape=(N,N) and if means.shape=(K,L) then covariance.shape=(K,L,K,L).) – lcovariance matrix of the multivariate log-normal distribution, i.e. covariance matrix of the underlying normal distribution of log(X)
flattener (
Flattener, optional, default=DummyFlattener() indicating no flattening) – The flattener encodes how to flatten the multidimensional properties stored in nD-arrays into a longer 1D-array for easiear error propagation. This flattener also allows to do the inverse transformation, i.e. deflatten the flattened 1D-array back to its original nD-array format. Should be specified if len(means.shape)=1 because it represents a flattened 2D array (which also implies len(covariance.shape)=2 because it represents a flattened 4D array).
- cov(unflatten=True)[source]
Compute and and return the covariance matrix of the MultiLogGaussian distribution.
- Parameters:
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return the covariance matrix in a shape equal to ‘the square’ of in the original dimensional shape. If False, return the covariance matrix as a flattened 2D array.
- classmethod exp_from_gaussian(gaussdist, shift=0.0, scale=1.0)[source]
Define the MultiLogGaussian distribution of a variable
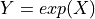 in which
in which 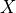 has a given MultiGaussian distribution, potential after imposing a shift and rescaling.
has a given MultiGaussian distribution, potential after imposing a shift and rescaling.- Parameters:
gaussdist (
GaussianDistribution) – the Gaussian distribution of variable X in the expression above.shift (float, optional, default=0.0) – shift to be applied to the mean upon conversion
scale (float, optional, default=1.0) – rescaling to be applied to the mean and std upon conversion
- Raises:
AssertionError – if the given gaussdist is not an instance of
MultiGaussianDistribution
- classmethod from_samples(samples, flattener=<thermolib.flatten.DummyFlattener object>, flattened=True)[source]
Defines a MultiLogGaussianDistribution based on a population defined by the given samples. The routine will derive the lmean and lcovariance from the population and use that to define the MultiLogGaussian Distribution.
- Parameters:
samples (np.ndarray) – the samples that define the population
flattened (bool, optional, default=False) –
If flattened is True, the given samples should be a 2D array in which a row represents all observations of a single variable and a column represents a single observation of all variables.
If flattened is False, then the the samples array is assumed to be 3 dimensional for which the first two dimensions represent a 2D index and the third index is the sample index. Therefore, the flattener will first be applied to flatten the 2D index into a 1D index and hence convert the samples to a 2D array of the same shape as required if the flattened argument is True.
- Raises:
AssertionError – if the dimensions of samples array are invalid
- mean(unflatten=True)[source]
Return the distribution mean
- Parameters:
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return the distribution mean in the original dimensional shape. If False, return the distribution mean as a flattened 1D array.
- Returns:
mean of the distibution
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- nsigma_conf_int(nsigma, unflatten=True)[source]
Compute the n-sigma confidence interval, i.e.
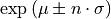
- Parameters:
nsigma (int, optional, default=2) – value of n in the above formula
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return the interval in the original dimensional shape. If False, return as a flattened 1D array.
- plot_corr_matrix(fn=None, fig_size_inches=[8, 8], cmap='bwr', logscale=False, cvs=None, nticks=10, decimals=1)[source]
gMake a plot of the correlation matrix of the current multivariate Gaussian distribution
- Parameters:
fn (_type_, optional, default=None) – file name to which figure will be saved. If None, figure will note be written to file.
fig_size_inches (list, optional, default=[8,8]) – [x,y]-dimensions of the figure in inches
cmap (str, optional, default='bwr') –
color map to be used, see matplotlib documentation to see possibilities.
logscale (bool, optional, default=False) – plot correlation in logarithmic scale
cvs (np.ndarray, optional, default=None) – set x and y-tick labels to CV values given in cvs
nticks (int, optional, default=10) – number of ticks on x and y-axis. Only used when parameter cvs is given.
decimals (int, optional, default=1) – number of decimals to be shown in CV tick labels. Only used when parameter cvs is given.
- sample(nsamples=None, unflatten=True)[source]
Returns a number of random samples from the population defined by the distribution
- Parameters:
nsamples (int or None, optional, default=None) – the number of samples returned. If None, a single sample will be returned with a shape depending on whether or not it is flattened (see parameter unflatten). If not None, the return value will have an additional dimension with size given by nsamples.
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return each distribution sample in the original dimensional shape. If False, return each sample as a flattened 1D array.
- Returns:
a (set of) random sample(s) from the population
- Return type:
np.ndarray whose dimension depend on the nsamples and unflatten keyword values. If nsamples is None, a single sample is returned whose shape depends on whether or not it is flattened (see parameter unflatten). If nsamples is not None, the return value will have an additinal dimension with size given by nsamples.
- std(unflatten=True)[source]
Return the distribution standard deviation (std)
- Parameters:
unflatten (bool, optional, default=True) – If True, return the distribution std in the original dimensional shape. If False, return the distribution std as a flattened 1D array.
- Returns:
standard deviation of the distibution
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- class thermolib.error.Propagator(ncycles=50, target_distribution=<class 'thermolib.error.GaussianDistribution'>, flattener=<thermolib.flatten.DummyFlattener object>, samples_are_flattened=False, verbose=False)[source]
A class to propagate the error distribution on a set of arguments towards the error distribution on a given function of those arguments. This routine uses the
sampleroutine of each of its distrubution arguments, meaning that the resulting error is stochastic (will not give the same repeated result).- Parameters:
ncycles (int, optional, default given by value of global variable ncycles_default) – the number of cycles for which a random sample is taken for each argument and corresponding function value is computed.
target_distribution (child class of
Distribution, optional, default=GaussianDistribution) – the type of distribution to be used for the error of the function value. Can be overwritten in the get_distribution routine.flattener (instance of child class of
Flattener, optional, default=DummyFlattener()) – Flattener to be parsed to the error distribution of the function value. Can be overwritten in the get_distribution routine.samples_are_flattened (bool, optional, default=False) – whether or not the samples generated by
gen_args_samples(and hence thesampleroutine of the arguments) are flattened. Can be overwritten in the get_distribution routine.verbose (bool, optional, default=False) – If True, increase verbosity of the propagator logging
- calc_fun_values(fun)[source]
Routine to compute the function value for each set of random samples stored for the arguments during execution of the
gen_args_samplesroutine.- Parameters:
fun (callable) – function f for which the error needs to be computed
- gen_args_samples(*args)[source]
Routine that will generate random samples for each of the given arguments. The total number of samples per argument is defined in self.ncycles.
- Parameters:
args (list of distributions) – list of arguments of the function for which the error needs to be computed
- get_distribution(target_distribution=None, flattener=None, samples_are_flattened=None)[source]
Routine to construct the error distribution of the function value from a population generated by the routines
gen_args_samplesandcalc_fun_values. For more info on arguments target_distribution, flattener or samples_are_flattened, see documentation in the initializer. Only if such an argument is explicitly specified (i.e. is not None), will it be overwritten with the given value.- Returns:
Distribution of the function value
- Return type:
determined by parameter target_distribution
- reset(target_distribution=None, flattener=None, samples_are_flattened=None)[source]
Reinitialize argsamples for future reuse. For more info on arguments target_distribution, flattener or samples_are_flattened, see documentation in the initializer. Only if such an argument is explicitly specified (i.e. is not None), will it be overwritten with the given value.
- class thermolib.error.SampleDistribution(samples)[source]
Define the distribution by explicitly supplying it with a population of samples. All statistical properties will be derived from this population.
- Parameters:
samples (np.ndarray) – the samples that define the population
- classmethod from_samples(samples)[source]
Defines the current SampleDistribution based on a population defined by the given samples. A trivial routine for the current class, but implemented for completeness of Distribution parent class.
- Parameters:
samples (np.ndarray) – the samples that define the population
- mean()[source]
Return the distribution mean
- Returns:
mean of the distibution
- Return type:
np.ndarray
- sample()[source]
Returns a random sample from the population given at initialization
- Returns:
a random sample from the population
- Return type:
np.ndarray or float
- set_ref(index=None, value=None)[source]
Set reference of population samples by shifting all population samples over an amount equal to -value.
- Parameters:
index – invalid keyword for SampleDistribution. Only valid value is None.
value (type consistent with population samples, optional, default=None) – old population value that will become new reference (i.e. become zero)
- Raises:
AssertionError – if index is not None
AssertionError – if value is None